
U.S. President Joe Biden and Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman during the Jeddah Security and Development Summit, in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, on July 16, 2022. Photo: Mandel Ngan/AFP via Getty Images
Despite the White House’s rhetoric about supporting global democracy, the U.S. sold weapons in 2022 to 57 percent of the world’s authoritarian regimes.
SINCE PRESIDENT JOE BIDEN came into office in 2021, he has described a “battle between democracies and autocracies” in which the U.S. and other democracies strive to create a peaceful world. The reality, however, is that the Biden administration has helped increase the military power of a large number of authoritarian countries. According to an Intercept review of recently released government data, the U.S. sold weapons to at least 57 percent of the world’s autocratic countries in 2022.
Since the end of the Cold War, the United States has been the world’s biggest weapons dealer, accounting for about 40 percent of all arms exports in a given year. In general, these exports are funded through grants or sales. There are two pathways for the latter category: foreign military sales and direct commercial sales.
How many of those countries were democracies, and how many were autocracies? That question can be answered by comparing the new U.S. arms sales data to political regime data from the Varieties of Democracy project at the University of Gothenburg in Sweden, which uses a classification system that’s called Regimes of the World.
The system classifies regimes into four categories: closed autocracy, electoral autocracy, electoral democracy, and liberal democracy. For a country to be classified as a democracy, it must have multiparty elections and political freedoms that make those elections meaningful. According to this methodology, the dividing line between democracies and autocracies is whether a country’s leaders are accountable to their citizens through free and fair elections.
Of the 84 countries codified as autocracies under the Regimes of the World system in 2022, the United States sold weapons to at least 48, or 57 percent, of them. The “at least” qualifier is necessary because several factors frustrate the accurate tracking of U.S. weapons sales. The State Department’s report of commercial arms sales during the fiscal year makes prodigious use of “various” in its recipients category; as a result, the specific recipients for nearly $11 billion in weapons sales are not disclosed.
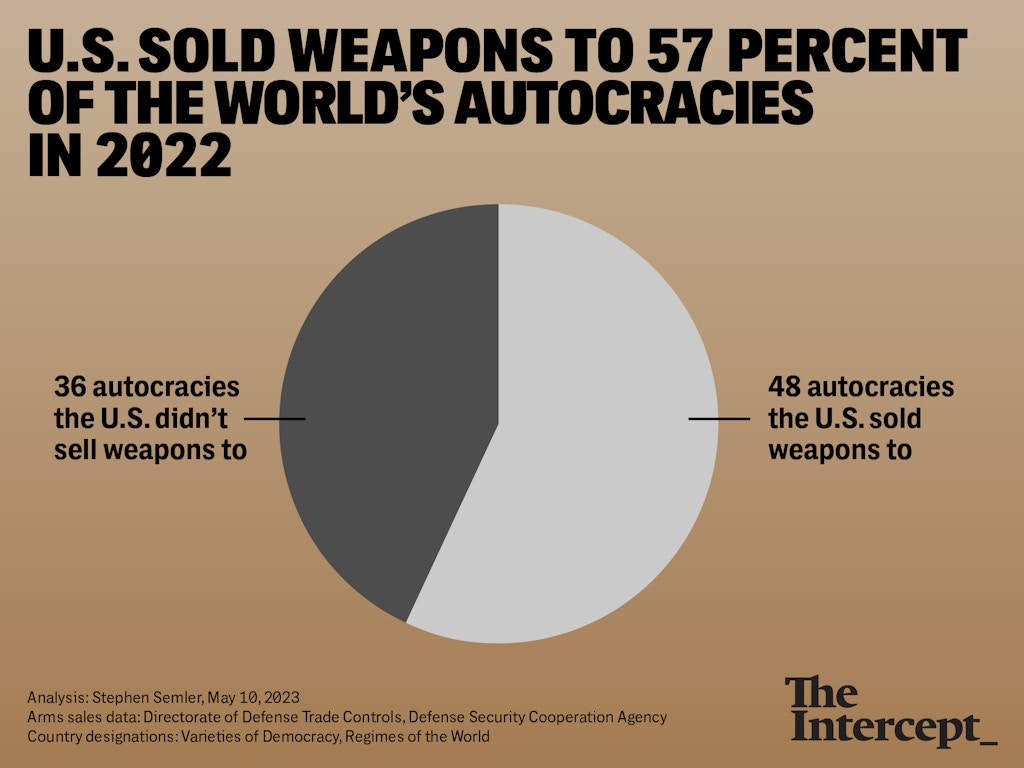
The Intercept’s review of recently released government data found that the U.S. sold weapons to 57 percent of the world’s autocracies in 2022.
Graphic: The Intercept
These findings contradict Biden’s preferred framing of international politics as fundamentally a struggle in which the world’s democracies, led by the United States, are on “the side of peace and security,” as he called it in last year’s State of the Union address. Opposing the United States and its democratic allies are the autocracies that collude to undermine the international system, Biden has stated. In a speech in Warsaw last year, he said the battle between democracy and autocracy is one “between liberty and repression” and “between a rules-based international order and one governed by brute force.” The White House’s 2022 National Security Strategy adds, “The most pressing strategic challenge facing our vision is from powers that layer authoritarian governance with a revisionist foreign policy.”
Despite that rhetoric, a review of the new data suggests instead a business-as-usual approach to weapons sales. Former President Donald Trump based his arms sales policy primarily on economic considerations: corporate interests above all else. In his first foreign trip as president, he traveled to Saudi Arabia and announced a major arms deal with the repressive kingdom. Trump’s business-first approach resulted in a dramatic upturn in weapons sales during his administration.
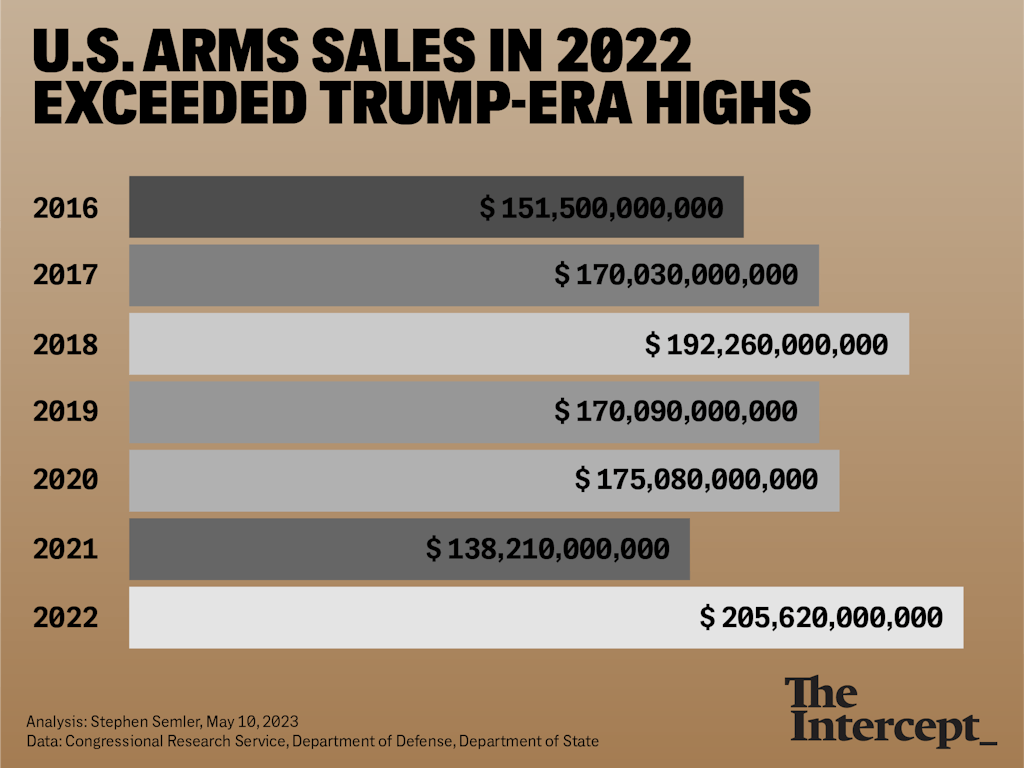
U.S. arms sales in 2022 exceeded Trump-era highs.
Graphic: The Intercept
Rather, the new figures reveal the continuity between Republican and Democratic administrations. While Biden signaled early on that his arms sales policy would be based primarily on strategic and human rights considerations, not just economic interests, he broke from that policy not too long after entering office by approving weapons sales to Egypt, Saudi Arabia, and other authoritarian regimes.

